Taphole casting materials for blast furnaces
2025-07-29
Definition of castable for blast furnace taphole
Currently, the main castable for blast furnace tapholes is ASC taphole castable---namely, Al2O3-SiC-C refractory material. Its aggregate is mostly corundum or alumina, the binder generally uses calcium aluminate cement, and the matrix often contains corundum, silicon carbide, carbon, and other additives. In practical use, it is generally made into a loose product according to the formula, then transported to the site, mixed with water, and finally cast and constructed.
Classification of blast furnace taphole castable
The Al2O3-SiC-C refractory materials for blast furnace tapholes developed by our company are divided into self-flowing castables, vibration castables, no-bake ramming materials, and prefabricated components. Castables and self-flowing materials are suitable for large blast furnaces, while no-bake ramming materials and prefabricated components are suitable for medium and small blast furnaces. These products have the characteristics of dense structure, high strength, good thermal shock resistance, and excellent slag erosion resistance. During use, they are resistant to scouring, corrosion, have a low melting loss rate, and high iron throughput.

|

|
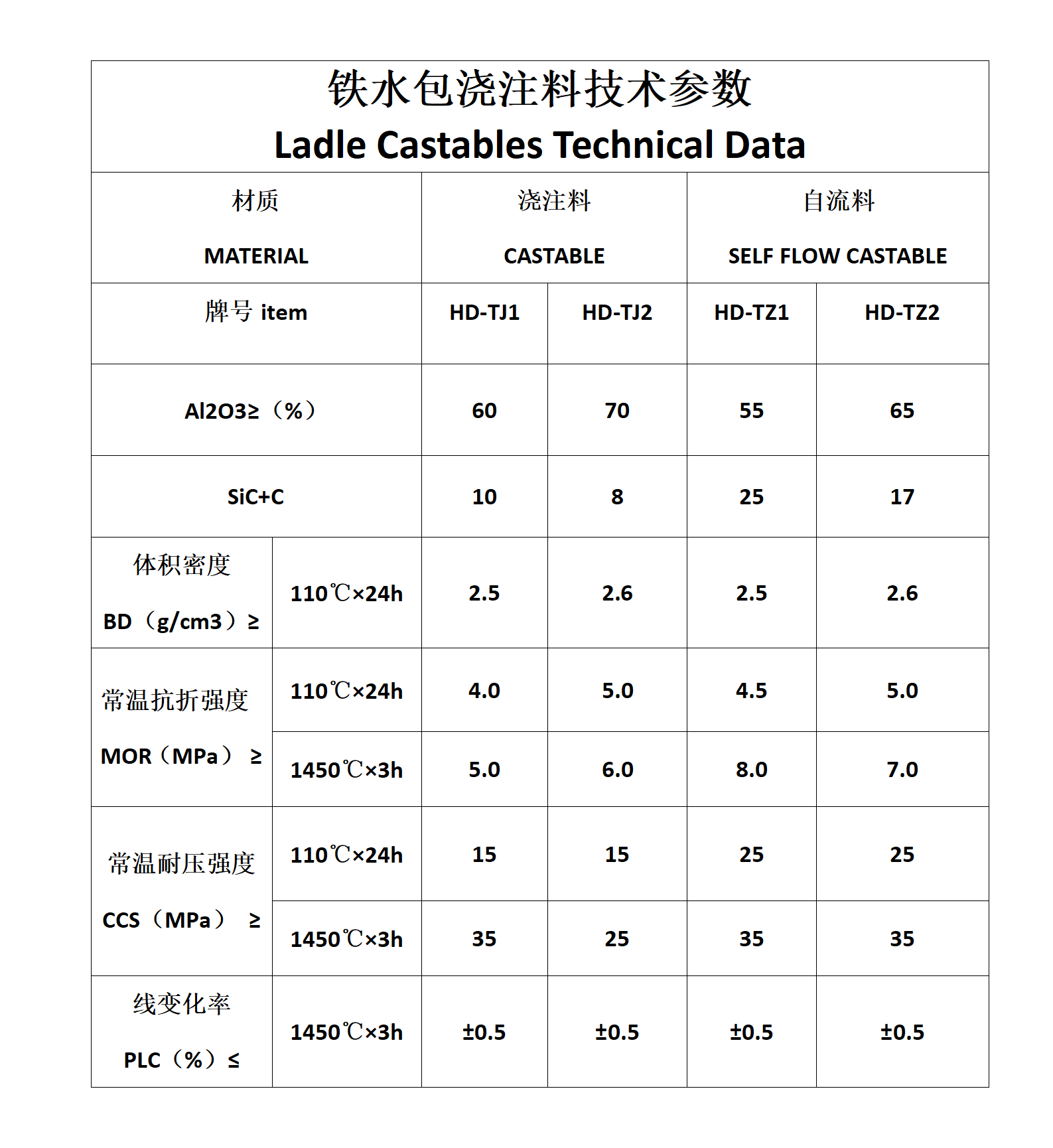
Technical parameters of blast furnace taphole castable
Construction methods of taphole castable
The construction methods of taphole castable are mainly integral casting or repair construction.
1 Integral casting
Integral casting is suitable for new tapholes or situations requiring complete replacement. Templates need to be set up according to the design slope. After mixing, the slurry is poured into the template and compacted by vibration. After curing, the required strength is achieved.
2 Repair construction
Repair construction is mainly used for local repair of existing tapholes. Usually, after the construction of the leveling layer at the bottom of the groove, the thickness of the subsequent layer is adjusted according to the actual elevation to ensure a tight interface.
3 Construction points
Material preparation: The amount of water added must be controlled according to the product instructions, and avoid making the mixture too thin or too thick during mixing;
Compaction by vibration: After casting, a vibrating rod must be used to vibrate and remove air bubbles;
Curing and baking: After construction, drying or steam curing must be carried out according to the specifications, and baking treatment must be carried out after the strength is reached.
Previous Page:



